Technical Article
Published 02/2024
Improving Electrical Switching Safety in the Resources Industry
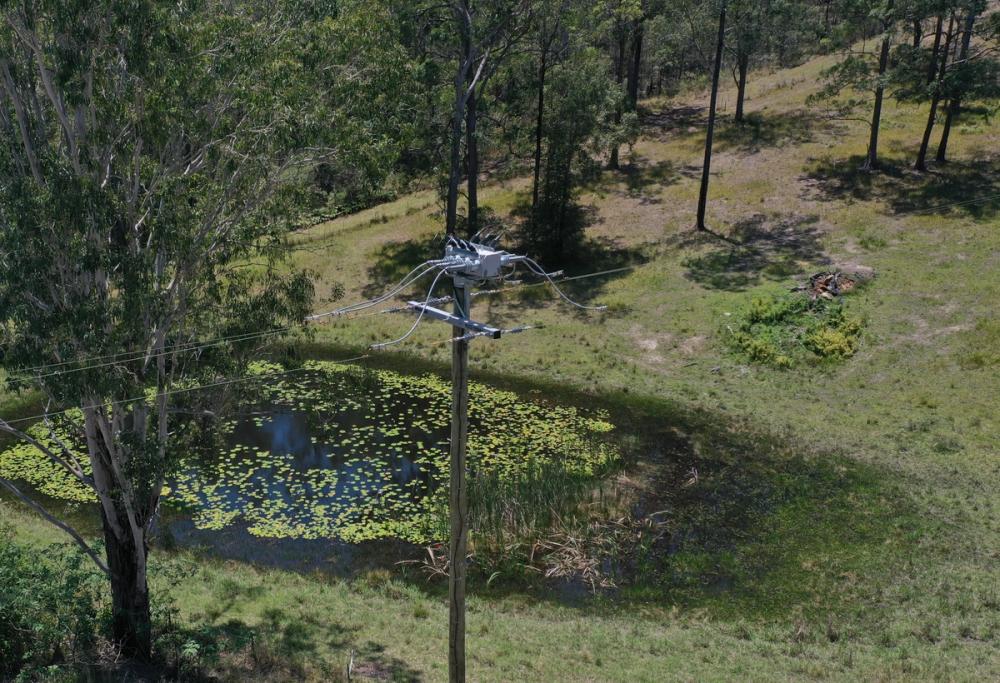

Switching Operations are essential for the reliability and functioning of electrical distribution grids. Networks which serve the resources industry, such as Mining or Oil and Gas networks bring added risks to the operations.
These industrial environments provide challenging operating conditions for electrical switchgear, where pollution buildup and high risk work environments can increase safety risks for operators.
However, these added risks are not unnoticed, and recent developments in electrical switchgear technology brings mitigations for these environmental risks, allowing resources operations to reduce downtime or frequency of workplace incidents.
The Operating Environment
Supplying power to assets on a resource site is a fundamental constraint of resource extraction. Processing plant or electrical excavation machinery does not generate revenue when it isn’t powered up.
These applications require reliable power, but the added high pollution environment increases the need for frequent maintenance. De-energisation of assets for maintenance access becomes routine in the reliable operation of a resource extraction enterprise.
This added pollution environment adds risk for traditional electrical switching equipment, or “Switchgear”.
Buildup of materials such as iron ore dust on legacy exposed air break switches can cause a degradation in performance or reliability.
While older designs of enclosed SF6 based load break switches mitigates the impact to isolation points, the industry ambition of carbon reduction is not compatible with using SF6 switchgear at the medium voltage distribution level.
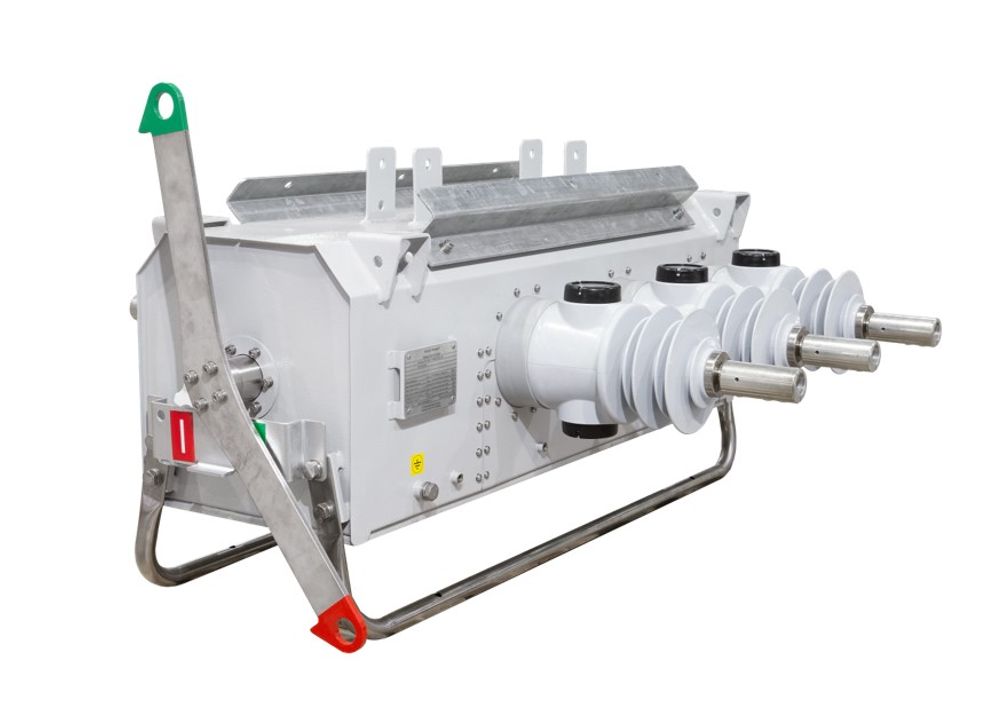
Fortunately, advances in solid dielectric insulation technology can offer a load break switch system which has zero SF6, but encloses the isolator for improved reliability performance in polluted environments.
How to improve electrical switching safety in resource extraction sites
One technique is to employ solid dielectric switchgear, rather than legacy air-break or SF6 insulated devices.
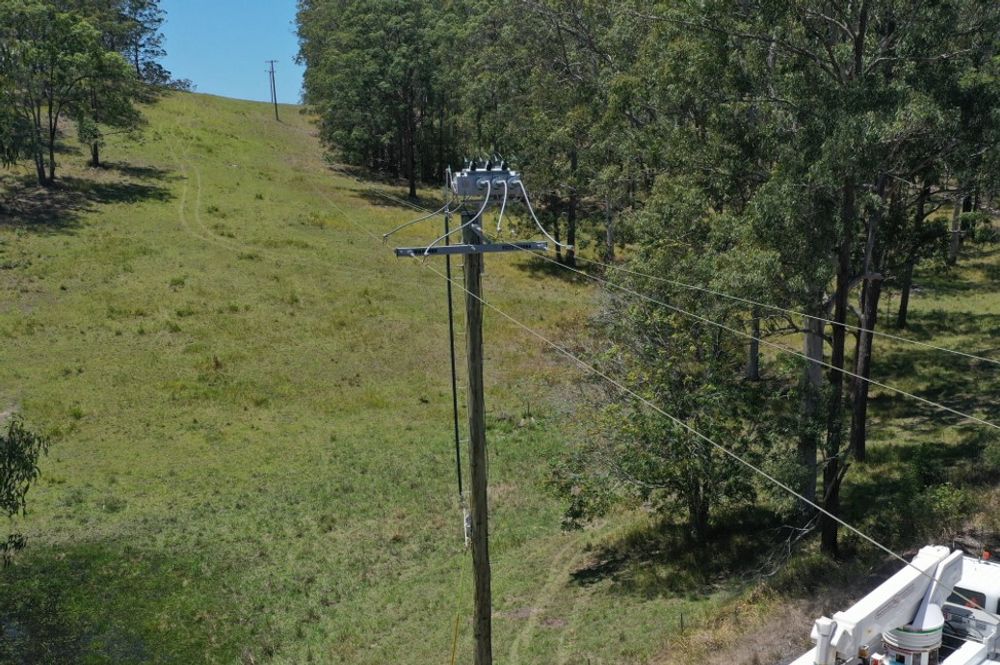

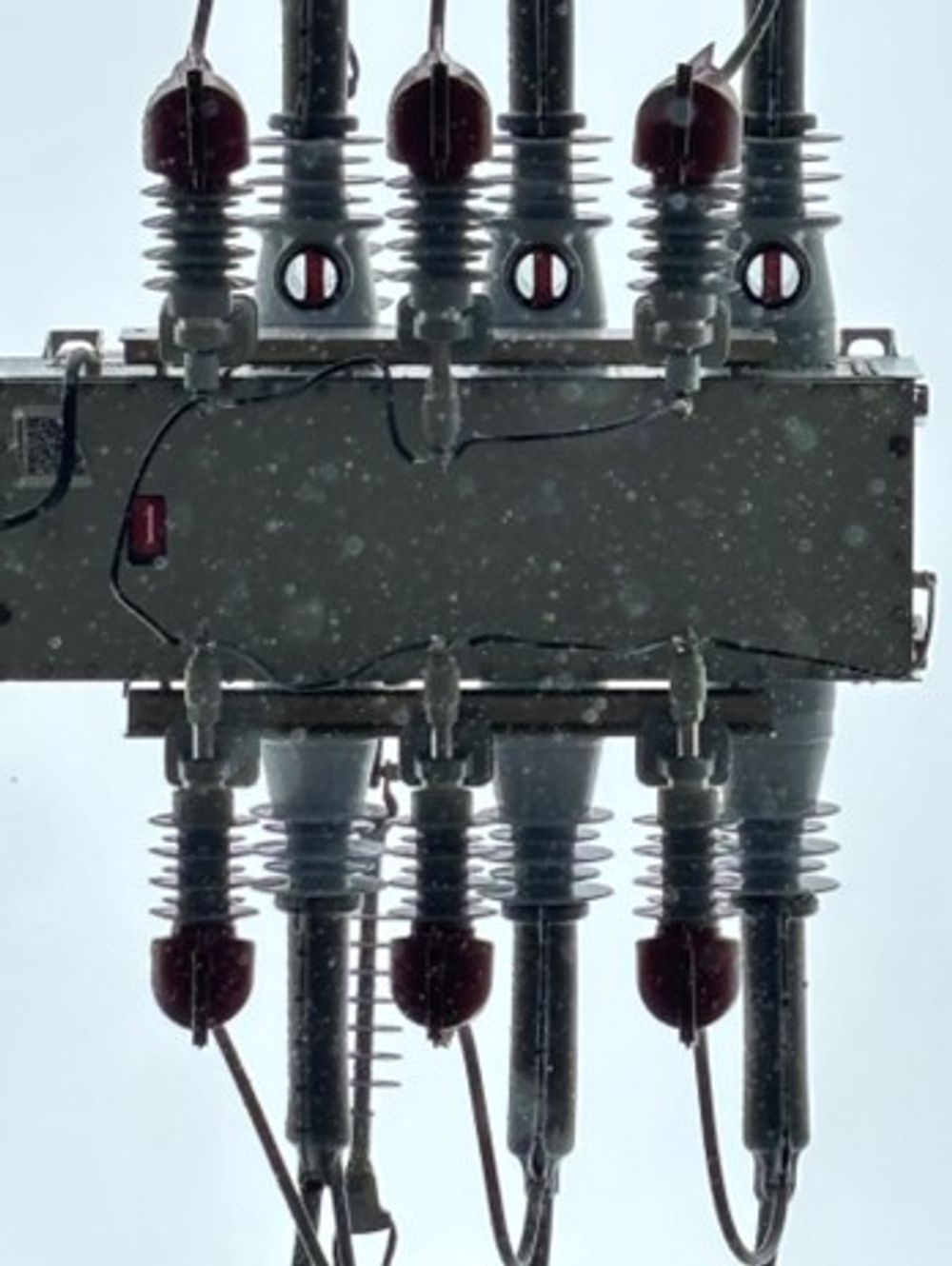
Medium voltage distribution switchgear such as the NOJA Power VISI-SWITCH® use a solid dielectric insulation scheme and enclose the isolation gap. This device also includes a viewing window for the isolation gap, affording operators the ability to confirm isolator position onsite, while greatly reducing the risk of pollution interfering with electrical performance.
This device also includes provisions for padlock style interlocking, making the equipment compatible with existing resources energy distribution works practices.
Deploying solid dielectric load break switches with an enclosed visible break offers a significant improvement to electrical switchgear safety, while also addressing decarbonisation objectives of the industry. Furthermore, these technology advancements in both safety and sustainability deliver a positive outcome for social license to operate.
Conclusion
“The NOJA Power VISI-SWITCH® allows our customers to buy a reliable enclosed load break switch that completely eliminates the use of SF6 gas and gives back operators the visible break they lost when open air-break switches stopped being used on distribution networks,” says NOJA Power Group Managing Director Neil O'Sullivan.
While resources industry applications accumulate additional operational risks, improvements in switchgear technology provide technical mitigations for the added risk.
Using enclosed solid dielectric load break switches provides an improvement in both safety and sustainability.
For more information, visit www.nojapower.com.

Want to stay up to date with Electrical Distribution Technology?
Join our list for a free weekly technical bulletin, as we share our Global Electrical Engineering experience directly to your inbox.
Subscribe →