Technical Article
Published 08/2019
Distributed Automation VII – Using IEC 61850 in Automation
Exploring Applications of IEC 61850 to the context of Distribution Network Automation

In our final instalment in the series of Electricity Distribution System Automation (DSA), we explore the relevance of IEC 61850 communications capabilities and how this technology can be applied to achieve reliability gains in the performance of the electricity network. Whilst IEC 61850 is traditionally considered confined to larger substations, IEC 61850 Generic Object Oriented Substation Event (GOOSE) Messaging has niche applications in achieving DSA when applied to distributed pole mounted switchgear.
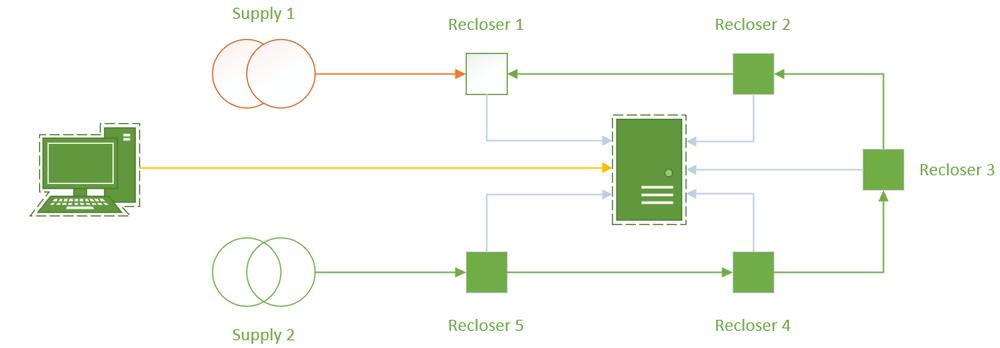
In our previous edition, we explored the performance of centralized automation and the applicability of the IEC 61499 PLC standard for sharing of information. Whilst IEC 61499 provides a method for communication of device status between Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs), the latency of performance lends its applicability to providing tailored data for centralized processing systems (such as in figure 1), rather than high performance peer to peer schemes.
GOOSE Messaging however is optimized for rapid distribution of messaging between IEDs. Distributed automation achieved at the IED asset site requires an extra close-onto-fault when communications are not present, but this can be resolved at high speed with using GOOSE messaging.
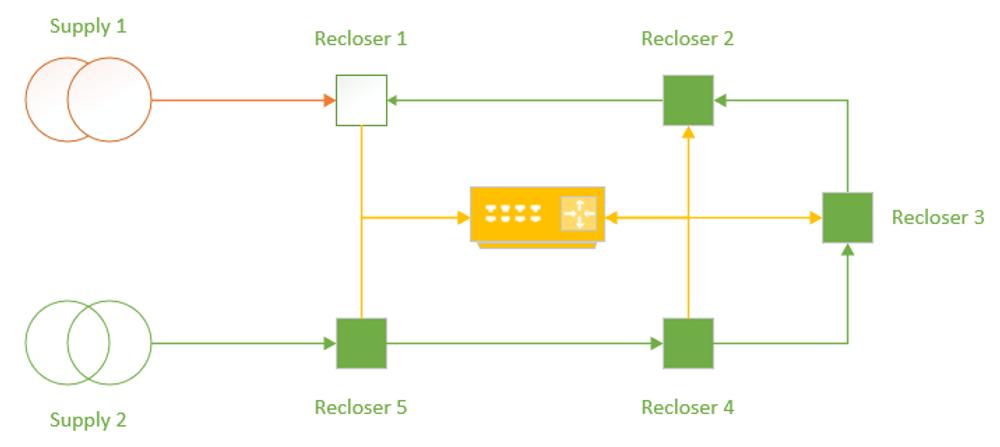
If the centralized system is redesigned as high-speed communications LAN, IEC 61850 GOOSE messaging can be used to publish trip and block commands to other connected devices based on the performance.
For instance, if Recloser 2 were to see a downstream fault condition, it could trip and issue a GOOSE message asking Recloser 3 to block the automation condition.
A further improvement would be if Recloser 1 trips on a fault between Recloser 1 and Recloser 2, it could issue a GOOSE message to trip Recloser 2 prior to the close operation of Recloser 3, providing fault isolation prior to supply restoration, minimizing fault reenergization impacts and providing optimum network re-switching to restore supply.
NOJA Power’s OSM Recloser system has IEC 61850 communications capabilities as standard, and when coupled with high speed communications between devices it can be used for comprehensive automation schemes employing blocking and tripping messages to optimize the performance of DSA.
“I believe this series of press releases on distribution automation has demonstrated the inbuilt automation capability in our products,” reports NOJA Power Group Managing Director Neil O’Sullivan. “Automation can be achieved without any communications network or higher-level automation can be achieved with either centralized or de-centralized communications systems with more investment in automation ultimately achieving higher gains in minutes of supply lost.”
This concludes our series on Distribution Automation. To recap on any of the past content, you can follow the links below.
- Automation I – Exploring Distribution Network Automation Options
- Automation II – Auto Changeover with P2P Communications
- Automation III – Distributed Automation
- Automation IV – Dealing with Network Grading
- Automation V – Centralized vs Distributed Automation
- Automation VI – IEC 61499 Smart Grid Automation
Want to stay up to date with Electrical Distribution Technology?
Join our list for a free weekly technical bulletin, as we share our Global Electrical Engineering experience directly to your inbox.
Subscribe →